Subtotal: $19.99
Spore Research: What is the best tool for the job?
Understanding the Differences Between Spore Syringes, Liquid Culture, Spore Prints, and Spore Swabs
The world of mushroom cultivation offers a variety of methods to propagate and grow mushrooms. Understanding the differences between spore syringes, liquid culture, spore prints, and spore swabs is crucial for both beginners and advanced growers. Each method has unique advantages and applications, depending on your cultivation goals.
Spore Syringes: A Gateway for Advanced Cultivators
Spore syringes are a popular choice among mushroom cultivators, especially for those experimenting with isolating unique mushroom characteristics. These syringes contain spores suspended in a sterile liquid, offering an effective way to start the mushroom-growing process.
- Why Choose Spore Syringes?: Spore syringes are ideal for advanced growers who want to explore the diverse genetic potential of mushrooms. When using spores, you can expect a variety of visually distinct mushrooms. This allows for the selection and tissue culture of the most desirable traits, such as cluster formation.
- The Challenge of Using Spore Syringes: While spore syringes offer diversity, they also require more time to achieve a harvest. The spores must germinate and pair to form mycelium, which then produces fruiting bodies. This process can take twice as long compared to using liquid culture.
- Advanced Tip for Spore Syringe Users: When germinating spores on an agar plate, look for rhizomorphic growth, which indicates the presence of fruiting bodies. Monokaryon mycelium, characterized by lighter, fluffy growth, does not produce fruiting bodies and should be avoided for cultivation.
Liquid Culture: The Fast Track to Mushroom Cultivation
Liquid culture (LC) is the preferred method for many growers due to its efficiency and reliability. Liquid culture syringes contain already isolated mycelium, which significantly speeds up the cultivation process.
- Benefits of Liquid Culture: Liquid culture is the quickest route to growing mushrooms. The mycelium in LC syringes has already been isolated, allowing it to propagate rapidly on grain and substrate. This method bypasses the initial steps required with spores, leading to faster colonization and fruiting.
- How to Create Liquid Culture: Liquid culture syringes can be made by cloning tissue from a favorable mushroom and adding it to a nutrient-rich liquid broth in a sterile environment. This method is particularly useful for growing strains that do not produce spores, such as certain designer magic mushroom strains.
- Considerations for Using Liquid Culture: While LC is easier to use, it requires careful sterile technique to avoid contamination. Liquid culture environments are highly susceptible to contamination, so working in a sterile manner is essential for successful cultivation.
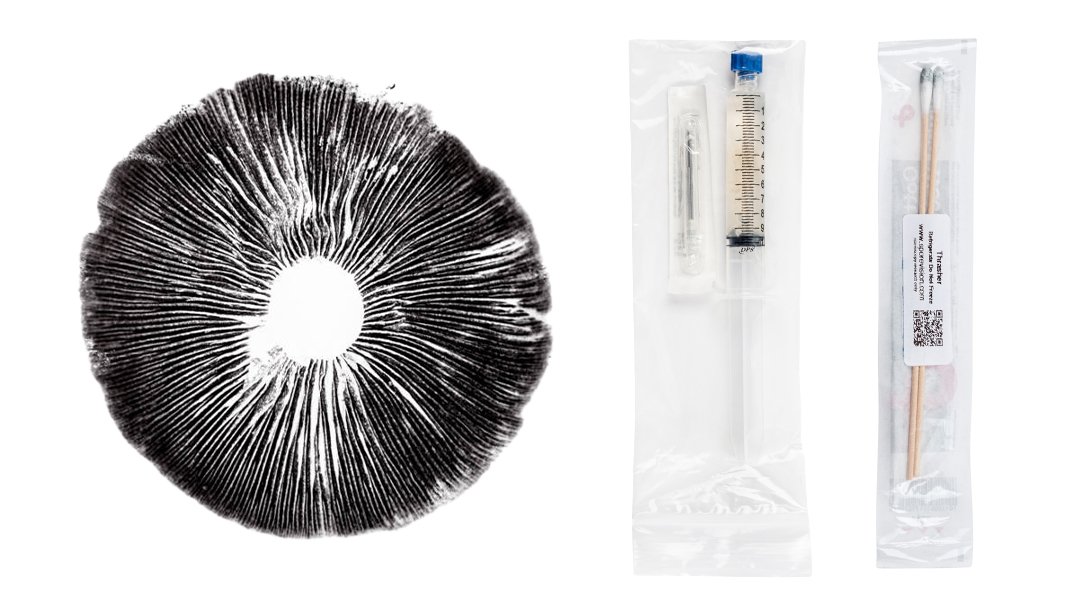
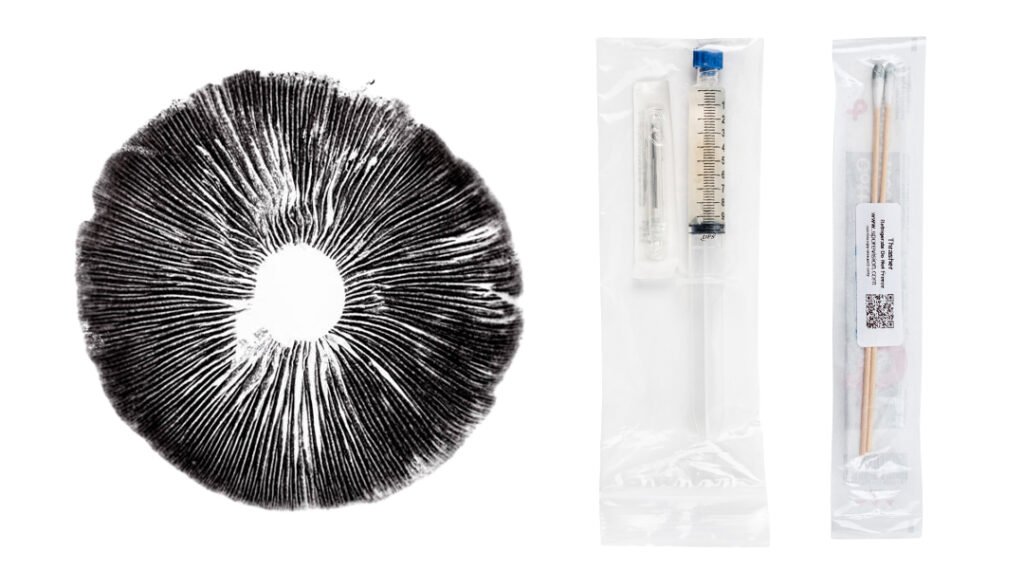
Spore Prints: Long-Term Storage and Genetic Exploration
Spore prints are a versatile tool for mushroom cultivation, offering a reliable method for long-term storage and genetic experimentation.
- Advantages of Spore Prints: Spore prints can be stored for years, even decades, in a refrigerator with minimal deterioration. They are invaluable for cross-breeding new strains and isolating specific characteristics, such as mushroom size and shape.
- How Spore Prints Are Used: Spore prints are used to create spore syringes by scraping the spores into sterile distilled water. These syringes are then tested on agar plates to ensure they produce viable mycelium. Spore prints are also an excellent way to ship and store genetics for future cultivation.
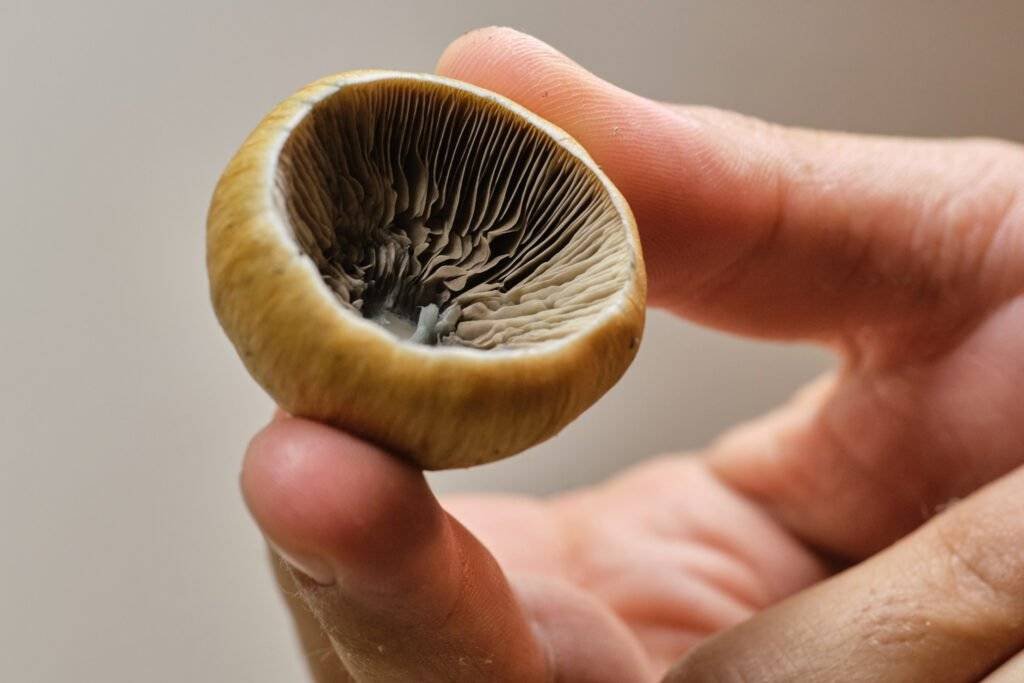

Spore Swabs: Preserving Unique Strains
Spore swabs offer an alternative method for preserving mushroom strains that do not easily drop spores, such as the penis envy and albino strains.
- What Are Spore Swabs?: Spore swabs are used to collect spores from mushroom caps that do not naturally release them. By rubbing a sterile cotton swab on the cap, growers can collect and preserve spores for future propagation.
- Benefits of Spore Swabs: Spore swabs are particularly useful for preserving genetics from strains bred to not drop spores. These swabs can be stored and later used to streak agar plates, ensuring the continuation of rare or valuable strains.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Mushroom Cultivation
The choice between spore syringes, liquid culture, spore prints, and spore swabs depends on your cultivation goals and the specific characteristics you wish to achieve.
- Spore Syringes and Prints for Diversity: If you’re looking to explore and isolate new traits, starting from spores with syringes or prints offers the greatest potential for genetic diversity and discovery.
- Liquid Culture for Speed and Reliability: For faster and more predictable results, liquid culture syringes are the way to go. This method is particularly advantageous for bulk production and strains that do not drop spores.
- Spore Swabs for Preserving Rare Strains: If you’re working with strains that don’t drop spores, spore swabs provide a practical solution for preserving and propagating these unique genetics.
Understanding the differences between these mushroom propagation methods is key to successful cultivation. Whether you’re an advanced grower seeking new strains or looking for a reliable way to grow mushrooms quickly, there’s a method suited to your needs.